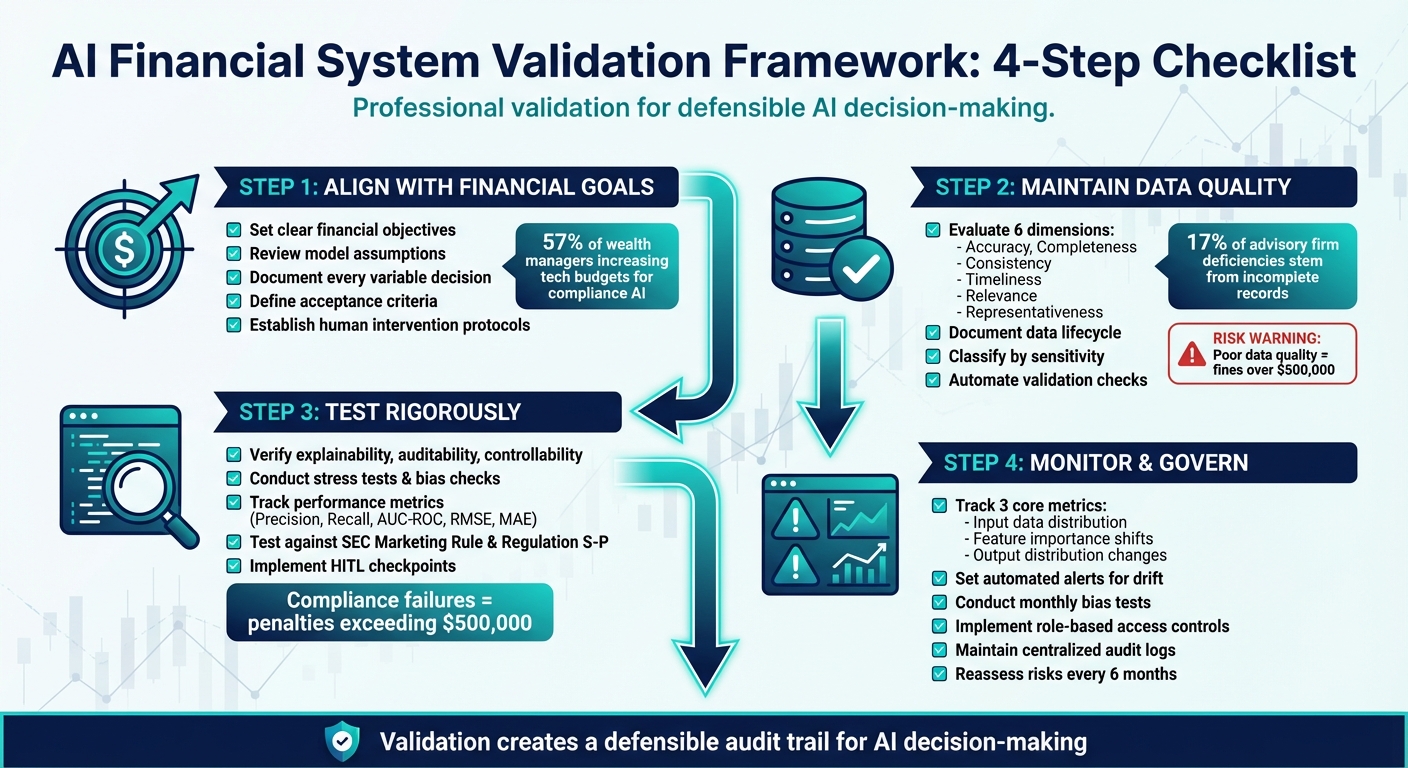
AI financial systems are changing how businesses operate, but validation is critical to ensure compliance, accuracy, and security. Without proper testing, companies risk fines over $500,000, reputational harm, and client loss. Here's what you need to know:
- Key Principles: Focus on explainability, auditability, and controllability to meet regulations like the SEC Marketing Rule and Regulation S-P.
- Data Quality: Evaluate data for accuracy, completeness, and relevance while documenting its lifecycle to avoid compliance risks.
- Testing: Validate models through stress tests, bias checks, and adherence to financial benchmarks.
- Governance: Monitor for model drift, enforce strict access controls, and maintain detailed audit trails.
These steps safeguard your systems and build trust in financial decision-making. Tools like Lucid Financials automate validation and compliance, making the process more efficient. Starting at $150/month, they offer real-time alerts, detailed data tracking, and investor-ready reporting.
AI Financial System Validation Framework: 4-Step Checklist
How to Evaluate an AI Use Case in Finance (Principles for Responsible and Effective Adoption)
Aligning AI Systems with Financial Goals
To get the most out of your AI system, start by identifying the specific financial problem it’s meant to solve. Without clear objectives, even the most advanced AI can turn into a costly misstep.
Setting Clear Financial Objectives
Your AI system should directly support measurable business outcomes. For example:
- Operational efficiency: Automating reconciliations or cutting down the time needed for period-end reporting.
- Strategic forecasting: Extracting insights from complex spreadsheets or running scenario analyses tailored for board presentations.
- Investment management: Optimizing portfolios with clearly defined rebalancing triggers.
- Risk mitigation: Establishing precise parameters for assessments and flagging edge cases where the model might struggle under real-world stress .
Consider this: 57% of wealth managers are increasing their tech budgets for compliance-focused AI solutions. This highlights the growing demand for validated systems that meet strict regulatory standards. Once you’ve defined your objectives, the next step is to review the assumptions baked into your AI model to ensure every variable serves those goals.
Reviewing Model Assumptions
Every variable in your AI model should connect directly to a documented business objective - it’s not just about accuracy; it’s about risk management. As FairPlay aptly puts it:
"Your P&L doesn't implode because you skipped a niche statistical test. It implodes when your model runs headfirst into the real world - with its steady lineup of 'unprecedented times' - and fails".
To avoid this, document every decision behind your model’s design. Why was each variable chosen? How were thresholds determined? What research supports these choices?. Define clear acceptance criteria before launching the system - specific performance metrics that determine success.
Additionally, establish protocols for human intervention. For instance, outline scenarios where a compliance officer or CFO should step in to override AI outputs. This “human-in-the-loop” strategy ensures that the system not only meets immediate operational needs but also aligns with long-term financial and fiduciary responsibilities.
Maintaining Data Quality and Integrity
An AI system is only as dependable as the data it processes. If the data quality is poor, the results can be inaccurate and even lead to compliance violations, which could cost firms over $500,000. The FINOS AI Governance Framework emphasizes this point:
"The integrity, security, and effectiveness of any AI system deployed within a financial institution are fundamentally dependent on the quality and appropriate handling of the data it uses".
To ensure your data supports reliable AI decisions, evaluate it across six critical dimensions: accuracy (error-free), completeness (no missing elements), consistency (uniformity across systems), timeliness (current and relevant), relevance (task-appropriate), and representativeness (reflects the target population without bias). These principles are not just theoretical - they are essential for defensible AI outcomes. For instance, state regulators have found that 17% of common deficiencies in advisory firms stem from incomplete records. This highlights how data gaps already pose a significant compliance risk, making robust data evaluation and management non-negotiable.
Evaluating Data Sources
Understanding your data's journey is critical. This means documenting its entire lifecycle - from how it was initially collected to every cleaning step, preprocessing decision, and feature engineering process. Such data lineage documentation provides the audit trail regulators will demand when questioning how your AI system reached a specific decision. Additionally, classify all data by sensitivity (e.g., Public, Internal, Confidential, Restricted) to ensure proper security measures are applied.
Before integrating new data sources, thoroughly vet them. Confirm their origin, verify existing quality controls, and assess classification accuracy. To maintain ongoing quality, use automated profiling and validation tools within your data pipelines to catch issues at scale. For highly sensitive data - like client account details or credit scoring inputs - pair automated checks with manual reviews conducted by compliance teams.
Managing Missing or Inconsistent Data
Missing or inconsistent data can disrupt even the most robust models. To prevent this, set up automated alerts that activate when data completeness or consistency falls below a pre-defined threshold. These alerts should halt model processing until the issue is resolved, ensuring corrupted data doesn’t compromise the system.
To address these gaps, follow standardized preprocessing practices. This includes handling missing values through imputation or removal, correcting errors, normalizing formats, and eliminating duplicates. Document all transformations to maintain a clear data lineage. Use feature attribution testing to identify which data points have the greatest impact on model outputs. This approach helps pinpoint where data quality issues could cause the most harm, allowing you to focus remediation efforts where they’re needed most.
Testing Processes and Outcomes
Once data quality and model alignment protocols are in place, the next step is to validate how well your AI performs in real-world financial scenarios. This involves rigorous testing to ensure both accuracy and reliability.
Verifying Implementation
After confirming data quality, focus on verifying that your AI system meets strict operational and compliance standards. Before going live, the AI must demonstrate three key capabilities: explainability (clearly outlining decision-making processes), auditability (maintaining detailed documentation of its development and deployment), and controllability (allowing human intervention or overrides when necessary).
Start by documenting the model architecture in straightforward, non-technical language. Fully map out the data lineage, tracing its path from collection through preprocessing to final input. Implement bias testing protocols to identify and address any discriminatory patterns before the system goes into production. Tools like SHAP can help explain individual predictions by showing which input features influenced specific outcomes.
Introduce human-in-the-loop (HITL) checkpoints for compliance officers to review or override AI decisions in high-stakes situations. Each intervention should be meticulously documented, with audit trails that can serve as critical evidence during regulatory reviews.
Once you’ve confirmed the system’s implementation integrity, shift focus to testing its performance under a variety of conditions.
Testing Performance and Benchmarks
Performance testing isn’t just about ensuring the system works - it’s about proving it can handle stress and maintain reliability. Conduct tests like adversarial scenarios, stress simulations, and input perturbations to identify vulnerabilities and weak spots in decision-making boundaries.
For classification tasks, track metrics such as precision, recall, and AUC-ROC. For regression tasks, focus on RMSE and MAE. Automate range and consistency checks to ensure outputs align with pre-established financial thresholds.
Regulatory compliance is equally critical. For example, if your AI generates marketing content, validate it against the SEC Marketing Rule (Rule 206-1). For systems managing client data, test compliance with Regulation S-P to ensure sensitive information isn’t inadvertently exposed. Considering that compliance failures have led to penalties exceeding $500,000, aligning your system with these regulations is not just a precaution - it’s a financial imperative. These rigorous evaluations confirm both the technical dependability of your AI and its adherence to financial regulatory standards.
sbb-itb-17e8ec9
Monitoring and Governance
Keeping a close eye on your AI models is essential to avoid model drift and stay compliant with regulations. Without proper monitoring, your model's accuracy can slip over time, leading to compliance issues and costly mistakes.
Detecting Drift and Setting Monitoring Protocols
There are three core metrics to keep tabs on: input data distribution, feature importance shifts, and output distribution changes. Monitoring input data ensures the data your model processes matches what it was trained on. Checking feature importance helps identify if the model begins prioritizing variables differently. Lastly, tracking output distribution flags any unusual deviations in predictions.
Set up automated alerts to notify you when these metrics stray from their established baselines. It’s also wise to watch for alignment drift caused by system updates. Using version pinning can help prevent unexpected changes sneaking in unnoticed.
Here’s a telling statistic: 57% of wealth managers have increased their tech budgets specifically for compliance solutions. To ensure fairness, conduct monthly bias tests across demographic factors, especially in areas like lending. This kind of ongoing monitoring connects your initial validation efforts with the governance demanded by financial regulations.
Implementing Governance and Compliance Measures
Strong governance starts with a clear framework: well-defined policies, documented processes, automated tools, and clear accountability. A centralized model inventory can serve as your go-to resource, keeping track of every AI project, its risk level, ownership, and monitoring status.
When drift is detected, your governance measures should kick in immediately, addressing and documenting these changes.
"Validation isn't just about checking boxes. It's about creating a defensible audit trail that demonstrates you understand your AI's decision-making process." - Luthor.ai
To tighten control, implement role-based access protocols so only authorized team members can modify model configurations or access sensitive training data. Log every step of your AI's lifecycle, from data collection to deployment and updates. Keep these logs detailed and centralized to meet regulatory scrutiny. Additionally, reassess risks every six months - AI evolves quickly, and regulations shift just as fast.
How Lucid Financials Simplifies AI Validation
Validating AI-driven financial systems is no small task. It demands ongoing monitoring, thorough documentation, and audit trails that can stand up to scrutiny. Lucid Financials tackles these challenges head-on by automating the creation of comprehensive evidence packages and maintaining detailed data lineage records. From the moment financial data is collected, through cleaning and preprocessing, to final model input, every step is meticulously documented. This robust foundation allows for precise and automated reconciliation processes.
Lucid’s AI-powered bookkeeping doesn’t just crunch numbers - it ensures accuracy by performing mathematical checks like footing and crossfooting while cross-verifying consistency between executive summaries and detailed footnotes. These automated processes significantly reduce the time it takes to close the books, cutting period-end durations down to just seven days while maintaining accuracy and compliance.
The platform also provides real-time risk notifications, ensuring potential issues like model drift or performance degradation are flagged immediately - long before they might be discovered during a quarterly review. Thanks to its Slack integration, founders can receive instant updates on critical metrics like runway, spending, and forecast accuracy. These AI-generated insights are further reviewed by seasoned finance professionals to ensure compliance and precision.
Lucid’s compliance-first approach extends to investor-ready reporting. With just one click, the platform generates reports that are structured, explainable, and ready for due diligence. Using interpretability techniques, every forecast is backed by clear explanations, making it easier to prepare for fundraising or handle audit requests without the last-minute scramble to compile documentation.
With pricing starting at $150/month, Lucid offers services tailored to your business’s growth stage - from basic bookkeeping to CFO-level forecasting and even tax credit optimization. While the AI adapts to your evolving needs, human experts step in to address complexities that algorithms might miss, ensuring your financial validation remains both efficient and defensible.
Key Takeaways
Validating AI financial systems is an ongoing process that creates a solid audit trail for your AI's decision-making. For startups and fast-growing companies, the stakes are high, but the process can be manageable with the right approach.
Focus on three key areas: explainability (understanding the reasoning behind decisions), auditability (keeping thorough documentation of development), and controllability (ensuring the ability to step in and adjust when necessary). Before deployment, take steps like documenting data lineage, explaining model architecture in simple terms, and running systematic bias tests. After launch, set up continuous monitoring to detect issues like model drift or performance drops early [1, 19].
Regulators are paying closer attention. Following the GAO's May 2025 warning about bias in financial AI tools, there’s increasing scrutiny on how companies protect against algorithmic discrimination. Rising compliance costs make efficient validation processes even more critical for growing businesses.
To simplify these tasks, tools like Lucid Financials help streamline validation. Their platform automates evidence package creation, tracks data lineage, and sends real-time risk alerts via Slack. Starting at $150/month, Lucid combines AI-powered automation with human oversight, offering an affordable solution for maintaining efficient, audit-ready validation.
A strong validation process not only protects your business from penalties but also fosters investor trust and ensures accurate, fair AI insights as your company grows.
FAQs
What are the essential steps to validate AI systems in financial operations?
Ensuring that AI systems function properly in financial operations requires a focus on accuracy, compliance, security, and reliability. The first step is to create a solid validation framework. This should include testing AI models to ensure they meet regulatory requirements, like adhering to SEC guidelines, and verifying that the data they use is accurate and easy to interpret. Regular risk assessments are also essential to spot and address any potential problems before the system goes live.
Another crucial element is setting up automated audit trails. These trails log all system interactions in real time, which not only boosts transparency but also simplifies compliance audits and reduces the chance of errors. Additionally, continuous monitoring and testing are necessary to confirm that the models perform consistently across different scenarios and can adjust to evolving regulations. Taking these steps helps businesses maintain trust and protect the integrity of their AI-powered financial systems.
How can companies maintain high-quality data in AI-driven financial systems?
To ensure reliable data in AI-powered financial systems, companies need a strong data governance framework. This means focusing on the accuracy, completeness, relevance, and timeliness of the data used in both training and operations. Establishing clear policies for handling and classifying data is key to managing sensitive information securely and responsibly.
Keeping track of data lineage and managing metadata are equally important. These practices make it easier to trace data sources and monitor changes, boosting both transparency and accountability. Regular checks and validation processes are vital for spotting and fixing errors or outdated data, which helps maintain the reliability of AI-driven decisions. By adopting these measures, businesses can strengthen trust in their AI systems while staying aligned with financial regulations.
How can businesses monitor and prevent model drift in AI financial systems?
To keep AI financial systems running smoothly and accurately, it's important to stay ahead of model drift. This happens when a model's performance changes over time due to shifts in data, concepts, or labels, potentially leading to less accurate predictions. To address this, businesses should focus on consistent monitoring, validation, and governance.
Start by regularly checking performance metrics like accuracy and relevance to spot early signs of drift. If you notice significant changes, it’s time to retrain or fine-tune the model to ensure it stays in sync with current data and business goals.
Another key step is setting up a governance framework. This means keeping clear records of data sources, model decisions, and validation results. Such documentation not only ensures transparency but also helps with compliance. Automated monitoring tools can make this process easier by sending real-time alerts when metrics fall outside acceptable ranges.
By staying proactive with these practices, businesses can ensure their AI systems remain dependable and aligned with financial objectives.